Hall sensor is a kind of magnetic field sensor based on Hall effect, which is widely used in industrial automation technology, detection technology and information processing. What is the working principle of the Hall sensor? What are the advantages of this sensor? What are the main parameters? This article will answer one by one.
(The essence of the Hall effect is that when the carriers in a solid material move in an external magnetic field, the Lorentz force acts to shift the trajectory and generate charge accumulation on both sides of the material, forming a current perpendicular to the current. The electric field in the direction eventually balances the Lorentz force and the electric field repulsion of the carrier, thereby establishing a stable potential difference (Hall voltage) on both sides.)
The Hall coefficient measured by the Hall effect experiment can determine important parameters such as conductivity type, carrier concentration, and carrier mobility of the semiconductor material.
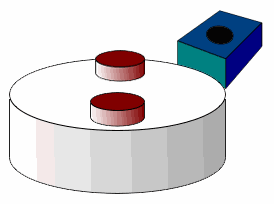
Since the potential difference generated by the Hall element is small, the Hall element and the amplifier circuit, the temperature compensation circuit, and the constant voltage power supply circuit are usually integrated on one chip, which is called a Hall sensor. The Hall sensor is also called a Hall IC and its shape is small, as shown in the following figure:
Hall sensor
Hall sensor advantages and uses
Many people know that the higher the degree of automation in cars, the more microelectronic circuits are, and the more they are afraid of electromagnetic interference. In the car, there are many lamps and electrical devices, especially the headlights with large power, air-conditioner motors and wiper motor will generate inrush current during switching, causing arcing of the mechanical switch contacts, resulting in greater electromagnetic interference signal.
Using power Hall switching circuits can reduce these phenomena. Hall devices can be used to monitor and measure changes in the operating parameters of various parts of a car by detecting magnetic field changes and converting them into electrical signals.
For example, position, displacement, angle, angular velocity, rotation speed, etc., and these variables can be transformed twice; pressure, mass, liquid level, flow rate, flow, etc. can be measured. The output of the Hall device is directly interfaced with the electronic control unit for automatic detection.
The current Hall devices can withstand a certain degree of vibration, and can work in the range of minus 40°C to minus 150°C. All the seals are not contaminated by water and oil, and can fully adapt to the harsh working environment of automobiles.
Hall sensors can measure arbitrary waveform currents and voltages, such as: DC, AC, pulse waveforms, and even transient peak measurements. The secondary current faithfully reflects the waveform of the primary current. The common transformer is not comparable to it, it is generally only suitable for measuring 50Hz sine wave
There is a good electrical isolation between the primary circuit and the secondary circuit, the isolation voltage can reach 9600Vrms;
High accuracy: The accuracy in the working temperature range is better than 1%, this accuracy is suitable for any waveform measurement; Hall switch devices are non-contact, no wear, clear output waveform, no jitter, no rebound, high position repeatability ( Up to μm class).
Wide bandwidth: The high bandwidth current sensor rise time can be less than 1μs; however, the voltage sensor bandwidth is narrow, generally within 15kHz, 6400Vrms high voltage voltage sensor rise time about 500uS, bandwidth about 700Hz.
Wide range of measurement: current measurement up to 50KA, voltage measurement up to 6400V.
Strong structure, small size, light weight, long life, easy installation, low power consumption, high frequency (up to 1MHZ), shock resistance, not afraid of dust, oil, water vapor and salt spray pollution or corrosion.
The above figure is a typical Hall sensor to achieve positioning applications - two magnets on one wheel go through the Hall effect sensor. The wheel in the illustration, with two equidistant magnets, the voltage on the sensor peaks twice in one cycle.
It is commonly used to measure the speed of wheels and shafts, for example on the ignition timing (timing) or tachometer of an internal combustion engine. Its use in brushless DC motors is used to detect the position of permanent magnets.
Hall sensors are widely used in inverters, inverters, UPS power supplies, communications power supplies, welding machines, electric locomotives, substations, numerical control machine tools, electroplating, computer monitoring, power grid monitoring, etc. Solar, wind and metro track signals, automotive electronics and other fields.
Hall sensor's main characteristic parameters
In the foregoing, the Hall sensor was introduced as a magnetic field sensor based on the Hall effect. Its main characteristic parameters are the following types.
(1) Input resistance R
The DC resistance of the two excitation current terminals of the Hall sensor element is called input resistance. Its value ranges from a few euros to hundreds of euros, depending on the type of component.
As the temperature rises, the input resistance becomes smaller, so that the input current becomes larger, eventually causing Hall sensor potential changes. To reduce this effect, it is best to use a constant current source as the excitation source.
(2) Output resistance R
The resistance between the output terminals of the two Hall sensors is called the output resistor, and its digits are in the same order of magnitude as the input resistors. It also changes with temperature changes. Selecting the appropriate load resistance is easy to match, which minimizes temperature-induced drift in the hydrodynamic potential.
(3) Maximum excitation current I - Hall sensor parameters
Since the Hall sensor potential increases with the increase of the excitation current, it is always desirable to use a larger excitation current of 1M in the application but the excitation current increases, the power consumption of the Chenger element increases, and the temperature of the element increases. As a result, the Hall sensor's temperature drift increases, so each part of the model specifies a corresponding maximum excitation current, which can range from a few milliamperes to hundreds of milliamps.
(4) Sensitivity K
Sensitivity KH=EH/IB, its value is about 10MV (MA.T).
(5) Maximum Magnetic Intensity BM---Hall Sensor Parameters
When the magnetic induction intensity exceeds BM, the nonlinear error of the Hall sensor potential will increase significantly, and the Tesla(T) becomes several thousand Gauss (Gs) (1Gs=104T).
(6) equal potentials
At rated excitation current F, when the applied magnetic field is zero, it is an error due to the asymmetry of the geometry of the 4 positive poles.
(7) Hall sensor temperature ratio
6M value is generally zero point knife Hall sensor output voltage between the open circuit is called the unequal potential, when used, more use of bridge method to compensate for the unequal potential caused by the date of a certain magnetic induction and excitation current, For every 1 degree Celsius change in temperature, the percentage change in the Hall sensor potential is weak as the Hall sensor potential temperature coefficient, which is related to the Hall sensor element material.
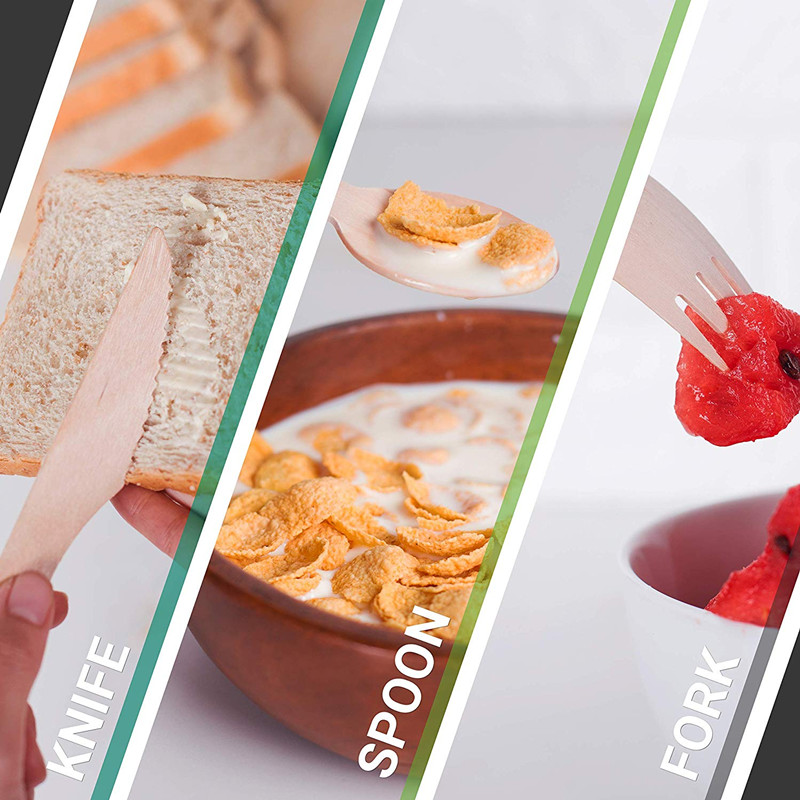
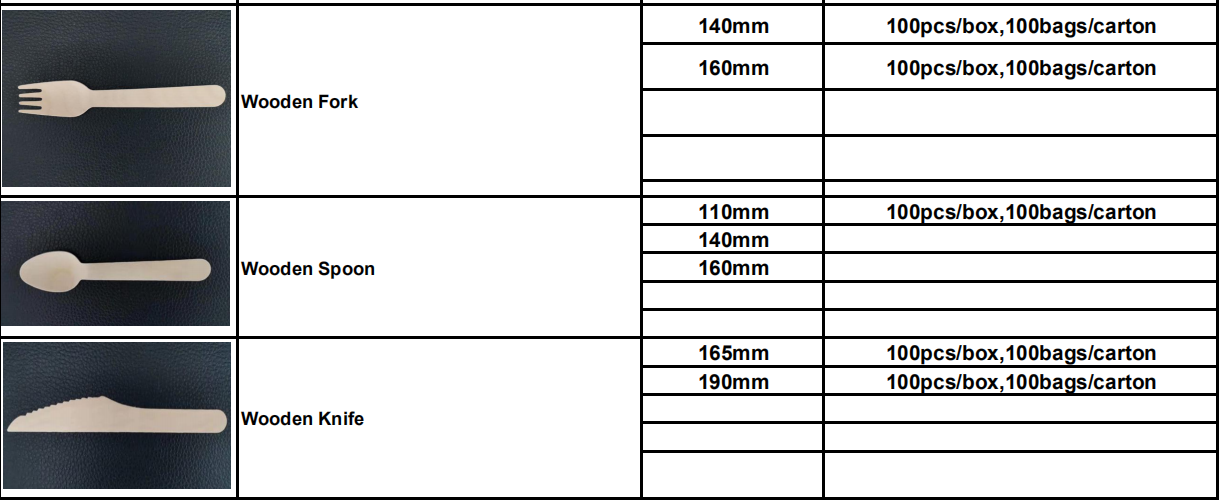
Wooden Kitchenware Knife
Wooden Kitchenware knife


FAQ
Q1: Are you manufacturer or trading company?
A1: We are manufacturer.
Q2: What is the material of products?
A2: Natural Birch.
Q3: How long will you deliver the products?
A3: 30~60 days after receiving 30% T/T deposit.
Q4: What is the payment term?
A4: T/T 30% as deposit in advance and balance 70% should be paid when goods ready to ship or L/C at sight.
Q5: Do you provide samples?
A5:Yes, free samples available.