Every day, your manufacturing process produce loose scrap, like turnings, filings, chips and shavings, that takes up valuable space. To maintain a clean, safe workplace, our Y83 series metal briquetting press could help. Briquetting your small scrap can reduce the volume as much as 90%, making scrap more economical to recycle or sell to foundries. It also help you to reclaim fluids, like oil, lubricants and other liquids. Briquette Making Machine, Briquetting Machine, Briquetting Press, Briquette Press, Block Making Machine Jiangyin Metallurgy Hydraulic Machinery Factory , https://www.eco-balers.com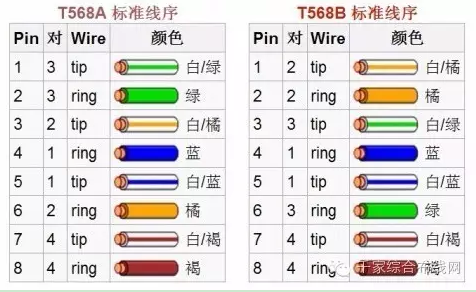

[Graphic] All kinds of twisted pair standard, usage, connection method shorthand
Various cable connector sequence
A cabling method is applied to the entire network cabling, but the network cabling with RJ45 ends at both ends is universal in the network regardless of whether it uses the termination method A or the termination method B. In practice, most use the T568B standard, which is generally considered to be better shielded against electromagnetic interference.
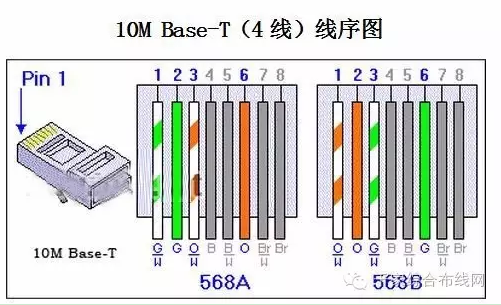
In addition, computer communication only uses the four lines of 1.2.3.6 (white orange, orange, white green, and green), and 10 Gigabit NICs. Gigabit NICs must have 8 lines. Therefore, four other lines can be used. As a telephone line, to save wiring costs.
Positive line (direct line): Both ends select the standard 568B line sequence
The order from left to right is (568B): white orange, orange, white green, blue, white blue, green, white brown, brown
The order from left to right is (568B): white orange, orange, white green, blue, white blue, green, white brown, brown
Network meter jump lights: 1 2 3 6 → 1 2 3 6
Anti-line (that is, cross-line): one end selects the 568B wire sequence, and the other end selects the 568A wire sequence
The order from left to right is (568B): white orange, orange, white green, blue, white blue, green, white brown, brown
The order from left to right is (568A): white green, green, white-orange, blue, white-blue, orange, white-brown, brown
Network meter jumping lights: 1 2 3 6 → 3 6 1 2
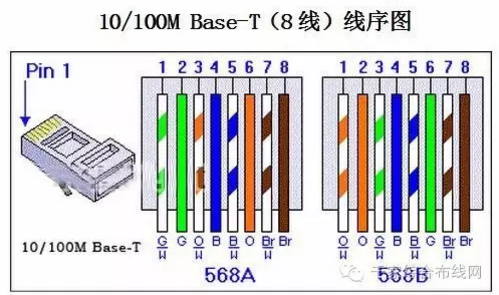
Positive line (direct line): Both ends select the standard 568B line sequence
The order from left to right is (568B): white orange, orange, white green, blue, white blue, green, white brown, brown
The order from left to right is (568B): white orange, orange, white green, blue, white blue, green, white brown, brown
Network meter jumping lights: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 → 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Anti-line (that is, cross-line): one end selects the 568B wire sequence, and the other end selects the 568A wire sequence
The order from left to right is (568B): white orange, orange, white green, blue, white blue, green, white brown, brown
The order from left to right is (568A): white green, green, white-orange, blue, white-blue, orange, white-brown, brown
Network meter jumping lights: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 → 3 6 1 4 5 2 7 8
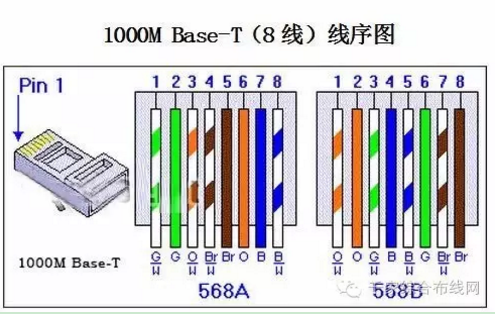
Positive line (direct line): Both ends select the standard 568B line sequence
The order from left to right is (568B): white orange, orange, white green, blue, white blue, green, white brown, brown
The order from left to right is (568B): white orange, orange, white green, blue, white blue, green, white brown, brown
Network meter jumping lights: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 → 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Anti-line (that is, cross-line): one end selects the 568B wire sequence, and the other end selects the 568A wire sequence
The order from left to right is (568B): white orange, orange, white green, blue, white blue, green, white brown, brown
The order from left to right is (568A): white green, green, white orange, white brown, brown, orange, blue, white and blue
Network meter jumping lights: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 → 3 6 1 7 8 2 4 5
The right choice of straight and cross lines:
PC represents the computer, HUB represents the hub, SWITCH represents the switch, and ROUTER represents the router.
PC-PC: Crossover
PC-HUB: Direct Line
HUB-HUB common port: Cross line
HUB-HUB (Common Port-Level Connection): Direct Line
HUB-HUB (level-interface-level connection): crossover
HUB-SWITCH: Crossover
HUB (Cascading Port)-SWITCH: Straight Line
SWITCH-SWITCH: Crossover
SWITCH-ROUTER: Direct Line
ROUTER-ROUTER: Crossover
Problems in the application of twisted pair in Gigabit network
1. Gigabit backbone switches, gigabit switches, what line? Category 6 (CAT6)
2. Gigabit backbone switch, connected to 100Mbps switch, what line? Category 6 (CAT6)
3. Gigabit backbone switches, new servers, what line? Category 6 (CAT6)
4. Gigabit backbone switch, access to the old server, what line? Category 5 (CAT5E), running 100Mbps
5. Gigabit switchboards, access to new machines, what line? More budget to use six types of lines (CAT6), at least use the five categories (CAT5E)
6. Hundreds of megabytes of switches, old machines, what line? With ultra-five. The original can not move, if the quality is too bad, then cut off, the new distribution of over five categories (CAT5E)
Common twisted pair
Twisted-pairs are generally classified into Category 3, Category 5 and Category 5, and the latest Category 6 line. The former has a narrow diameter and the latter has a coarse diameter.
1) One type of line: mainly used for voice transmission (a type of standard is mainly used for telephone cables before the early 1980s), unlike data transmission.
2) Second-category line: The transmission frequency is 1 MHz. It is used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 4 Mbps. Commonly used in old tokens using the 4 MBPS specification token transfer protocol?
3) Category 3: Refers to the cable currently specified in the ANSI and EIA/TIA 568 standards. The transmission frequency of the cable is 16 MHz. The data transmission used for voice transmission and the maximum transmission rate of 10 Mbps is mainly used for 10BASE--T.
4) Category IV: The transmission frequency of this type of cable is 20MHz. The data transmission for voice transmission and the maximum transmission rate of 16Mbps is mainly used for token-based LAN and 10BASE-T/100BASE-T.
5) Category 5 cable: This type of cable increases the winding density and coats a high quality insulating material with a transmission rate of 100 MHz for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 10 Mbps, mainly for 100BASE-T and 10BASE-T network. This is the most commonly used Ethernet cables.
6) Super Category 5: Super Category 5 has small attenuation, low crosstalk, and higher attenuation and crosstalk ratio (ACR) and signal-to-noise ratio (Structural Return Loss), smaller delay error, and very good performance. Greatly improved. Category 5 is mainly used for Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps).
7) Category 6 cable: The transmission frequency of this type of cable is from 1MHz to 250MHz, and the PS-ACR of the Category 6 cabling system should have a large margin. It provides 2 times the super-five. bandwidth. The transmission performance of the six types of cabling is much higher than the super five standard, and is most suitable for applications with a transmission rate higher than 1 Gbps.
An important difference between Category 6 and Category 5 is that it improves performance in terms of crosstalk and return loss. For a new generation of full-duplex high-speed network applications, excellent return loss performance is extremely important. The basic link model has been eliminated from the six types of standards. The wiring standard adopts a star topology. The required wiring distance is: the length of the permanent link cannot exceed 90m, and the length of the channel cannot exceed 100m.
At present, twisted pair can be divided into unshielded twisted pair (UTP = UNSHILDED TWISTED PAIR) and shielded twisted pair (STP = SHIELDED TWISTED PAIR). The outer layer of the shielded twisted pair cable is wrapped with aluminum foil to reduce radiation, but it does not completely eliminate radiation. The shielded twisted pair is relatively expensive and is more difficult to install than unshielded twisted pair cables.