â‘ Hardness:
Due to the scientific synthesis of high-molecular polyurethane elastomer materials using iron rubber, the higher the hardness, the higher the modulus, the smaller the elongation, and the better the wear resistance and heat resistance. Well, in the range of minus 35 degrees Celsius to 100 degrees Celsius, and at a pressure of 60 to 70 MPa, the maximum sealing performance can be guaranteed.
The use of viscoelastic seals made of nitrile rubber is the most complete protection against damage caused by back pressure. In the range of minus 55 degrees Celsius to 100 degrees Celsius, and under a pressure of 21MPa, due to the rubber The seal is often in a compressed state, so the compression performance of the rubber seal must be considered. It not only achieves enhanced anti-climbing performance and low friction resistance, but also has good performance in dealing with special low-temperature oil, and can also be used in combination with Anti-wear Ring double-purpose retaining ring BRL type.
Sealing products made of polytetrafluoroethylene and nitrile rubber/PTFErubber; or seals made of nylon resin and nitrile rubber, which can be used in a wide range of applications with large pressure changes and fast sliding speeds According to the working condition, the input hydraulic pressure cutout is designed on the end face of the polytetrafluoroethylene ring to prevent penetration leakage. The maximum working temperature environment is minus 40 degrees Celsius to 160 degrees Celsius; the maximum working pressure is 50MPa.
oil seals,hydraulic oil seal,track link oil seal,TCV oil seal,O-ring Safe Seal Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jolseals.com
The first is the challenge from the flame retardant. Most of the flame retardants currently used are halogen derivatives or antimony-containing flame retardants. The presence of halogen-based flame retardants can cause many problems, such as the generation of toxic gases that harm the human body and the environment when burned. Such as dioxin, benzofuran, etc., these toxic gases may cause the body's metabolic disorders, resulting in tension, insomnia, headache, eye diseases, arteriosclerosis, liver tumors and other symptoms, animal experiments have led to cancer; On the other hand, it is also very difficult to treat or recover these halogen-containing wastes. Therefore, the use of halogen-containing flame retardants has been greatly limited. The European Union had already completed the draft revision of the fifth edition of the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Treatment Act as early as June 2000. It regulates halogen-free electronic materials and specifies chemical substances such as PBB and PBDE. It is banned on January 1st.
The challenge from lead-free solders cannot be ignored either. Acid rain in the nature will dissolve the lead materials in the solder. Lead and lead through the food and drinking water will accumulate in the human body, causing heavy metal pollution and endangering human health. Therefore, the lead-containing additives have also become strictly prohibited in the EU WEEE. In line with environmental protection requirements, the development of lead-free solder has become an inevitable trend. The lead-free solder currently developed has a relatively high melting point, so the reflow peak temperature has also increased from 230 to 245° C., which is currently a lead-containing solder, to 250 to 265° C. Then there is the pick from the packaging process. In recent years, the semiconductor packaging technology field is undergoing two major changes and contains the third change. The first change took place in the early 1970s. It was typically characterized by the transformation of the packaging style from plug-in (such as DIP) to surface mount (such as QFP); the second revolution occurred in the mid-1990s. Characterized by the transition from a four-sided leaded surface mount (eg, QFP) to a planar array surface mount (eg, BGA).
The third change that appeared in the early 21st century has already begun to emerge. Its typical features are chip size package (CSP), three-dimensional stacked package, and all-silicon wafer package. During these three transformations, the role of packaging materials will become more and more important, and it has been regarded as the decisive factor in exploiting the limit (optimum) performance of integrated circuits. The development of new packaging technology has put forward the following basic performance requirements for epoxy molding compound: high heat resistance, low moisture absorption, low stress and low cost. As with many other organic polymer materials, epoxy resins are also easy to burn. Therefore, flame retardants are usually added during use. Traditional epoxy resin sealants are difficult to meet the above requirements at the same time. Therefore, high-performance epoxy resin sealants are developed. It is imperative.


SPGW piston seal
Material:PTFE+rubber elastomer+reinforced modified nylon
Temperature:Nitrile rubber -40~100℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤50mpa
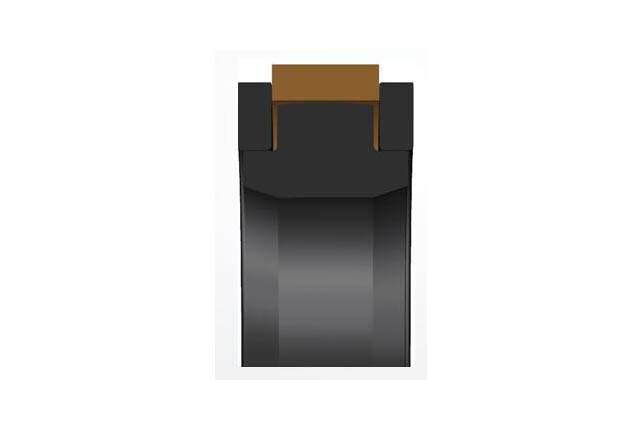
SPGO piston seal
Material:PTFE+rubber elastomer
Temperature:Nitrile rubber -40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤35mpa
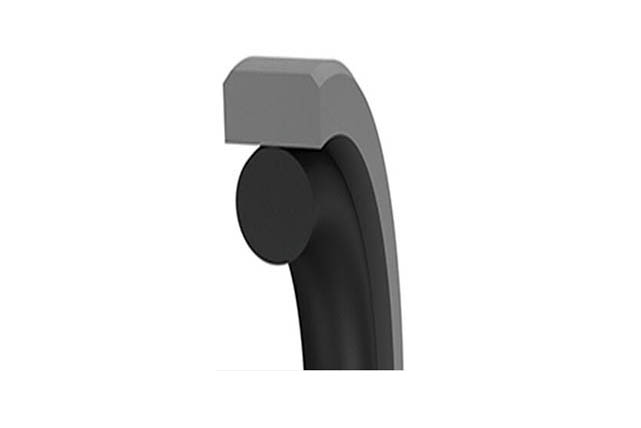

SRUV piston rod seal
Material:NBR+thermoplastic polyurethane
Temperature: -35`90℃
Speed:=0.5m/s
Pressure:≤40mpa
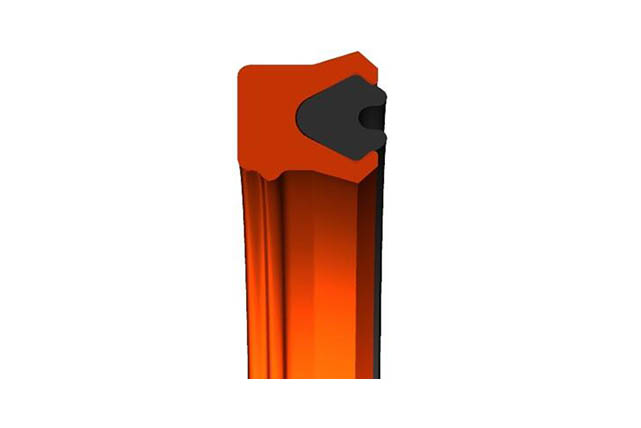

SRS piston rod seal
Material:PTFE+NBR
Temperature:-40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤40mpa
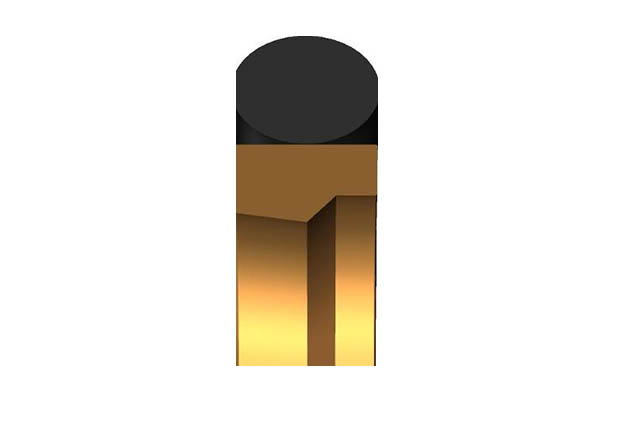

SRCB piston rod buffer seal
Material:Polyurethane+modified polyoxymethylene
Temperature: -35~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤50mpa
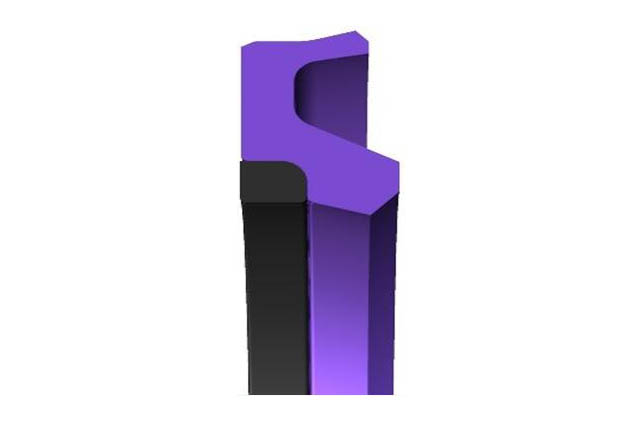

SRU piston rod seal
Material:Polyurethane
Temperature:-35~100℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤40mpa
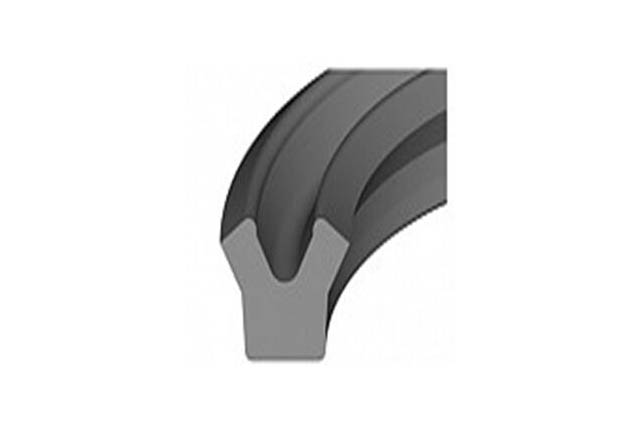

SRD iron case dust prevention
Material:Polyurethane+metal skeleton material
Temperature:-40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
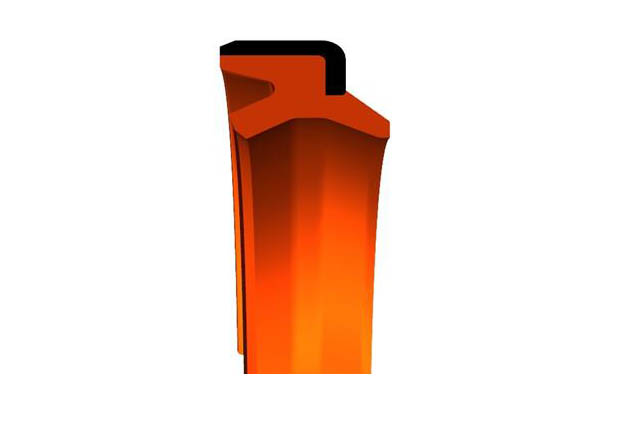

SRDI soft dustproof
Material:polyurethane
Temperature:-40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/
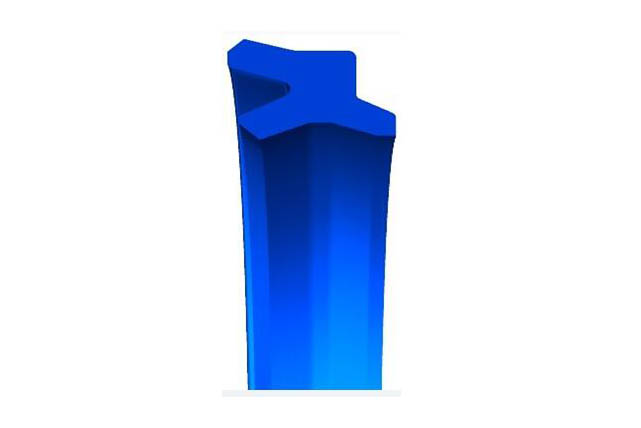

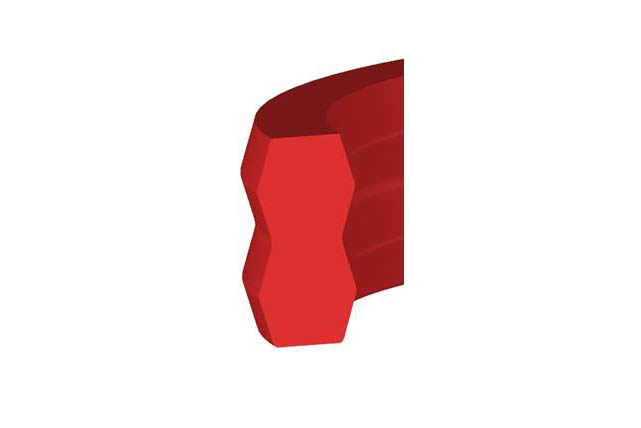
SDS Dumbbell Seal
Material:polyurethane
Temperature: -35~110℃
Speed:=0.5m/s
Pressure:≤50mpa
SPG piston combination seal
Temperature:
NBR+Polyurethane + Modified Polyoxymethylene
Temperature:-35`110℃
Speed:=0.3m/s
Pressure:≤70mpa
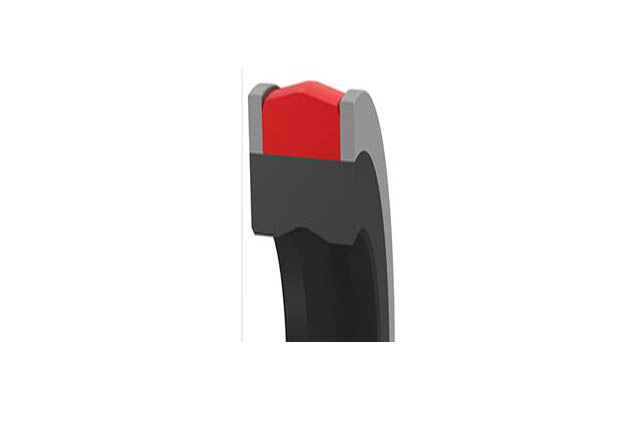

SRNL piston rod seal
Material
NBR+Polyurethane + Modified Polyoxymethylene
Temperature:-35`110℃
Speed:=0.3m/s
Pressure:≤70mpa
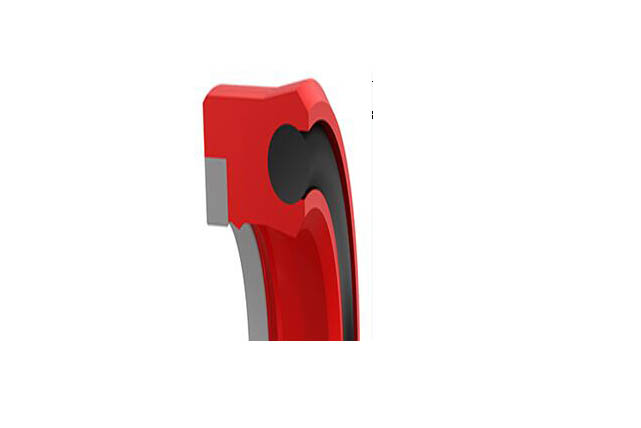

SRDF Piston Rod Seal
Material
Polyester rubber
Temperature:-40`100℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
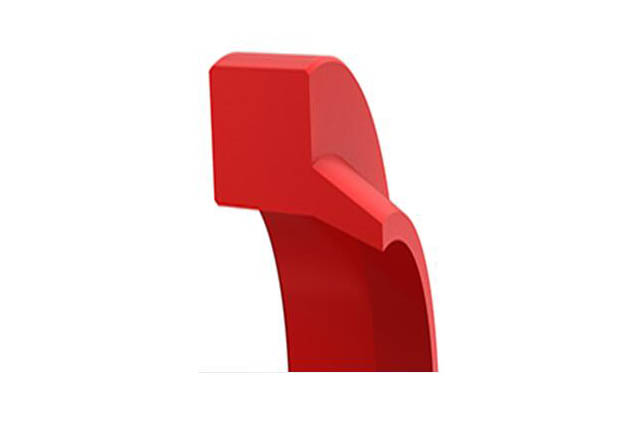

SDY Y-seal
Material:Polyurethane
Temperature:-35~110℃
Speed:=0.5m/s
Pressure:≤70mpa
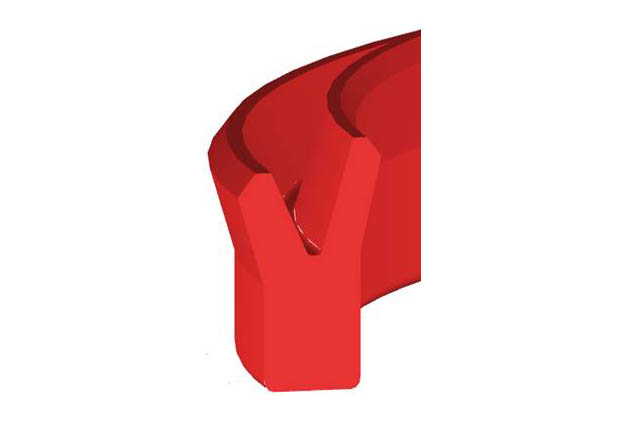

KZT anti fouling ring

SDS Steffel

Piston main oil seal

Traditional epoxy plastic materials industry will face enormous challenges
Epoxy resin composites are mainly composed of epoxy resin, crosslinking curing agent, curing accelerator and additives, etc. It has many outstanding characteristics, such as good thermal stability, insulation, adhesion, good mechanical properties. , excellent molding process performance and lower costs, etc., are widely used in the field of electronic components bonding, packaging and printed circuit board production, and thus become one of the most important electronic chemical materials. Epoxy resin composites can be divided into various types such as epoxy molding compound (EMC), PWBs base material, and electronic component bonding material (conductive adhesive, thermal conductive adhesive, patch adhesive) according to different fields of application. In recent years, with the continuous development of advanced microelectronics technology and the rising popularity of environmental protection worldwide, the demand for environmentally friendly epoxy resin compounds is increasing, and traditional epoxy composites are facing enormous challenges in many aspects. challenge.