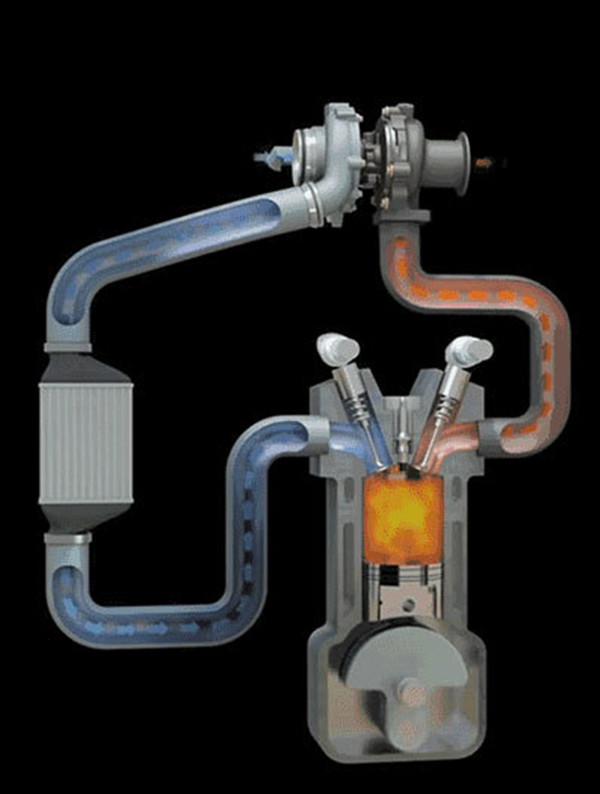
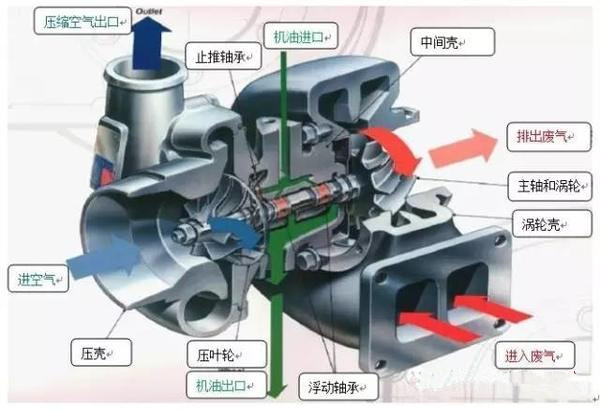
Now when it comes to selling cars, no matter whether it is a cart or a turbine, it must be scorned by its peers. So what is this miracle turbine? Is it really synonymous with high technology? In 1905, Dr. Alfred J Buchi, chief engineer of the Sulzer Brothers R&D Company in Switzerland, presented the concept of turbocharging for the first time. Turbocharging technology was born and applied to ships. And aerospace engineering. In 1953, the Garrett Company of the United States applied turbocharging technology to vehicle diesel engines. After the 1960s, turbochargers were widely used in foreign vehicle diesel engines. After the 1980s, gasoline engines also began to use turbocharger technology. One, supercharger principle We know that the diesel engine's work requires diesel and air to generate heat and convert it into mechanical energy before it can output power. The theoretical air-fuel ratio of diesel to air is 1:17, but the actual combustion requires a certain excess air coefficient, naturally aspirating the diesel engine. The air-fuel ratio cannot satisfy good combustion, and the intake pressure booster is a necessary measure to meet the required combustion efficiency to achieve good combustion. The exhaust gas turbocharging system is our most common turbocharging device and is actually an air compressor that increases the intake air volume by compressing the air. It uses the inertial impulse of the exhaust gas emitted by the engine to propel the turbine in the turbine shell. The turbine drives the impeller in the coaxial compressor. The impeller compresses the inhaled air, that is, it is pressurized to enter the cylinder, and the air density in the cylinder is increased. The increase in density can burn more fuel, so that when the engine displacement is constant, the output power is increased, and the combustion efficiency is greatly increased. The CO2 discharged into the atmosphere and harmful substances such as NOx are greatly reduced, and it is very environmentally friendly. The key role. The advantages of using a turbocharger: – Increased engine power and greater output power - Reduce fuel consumption while reducing CO2 emissions – Reduce NOx, HC, and CO exhaust pollutants, completely eliminate black smoke, and meet emission regulations Second, the supercharger structure The exhaust gas turbocharger consists of an exhaust gas-driven turbine and a radial compressor, which are respectively mounted on both ends of the shaft and have respective cast shells. The shaft itself is mounted in the middle shell and supported by the middle shell. The two sides of the middle shell are respectively connected with the compressor shell and the turbine shell, and the typical turbocharger speed can be more than 100,000 rpm. – Turbine end: Exhaust gas enters the turbine end, propels the turbine to rotate – Spindle: The main shaft connects the turbine and the pressure impeller to transfer kinetic energy – Intermediate shell: connecting turbine end and pressure end, supporting bearing system – Compressor end: pressure impeller rotates compressed air to increase air-fuel ratio – Bearing system: Supports high-speed rotation of the spindle to prevent radial misalignment of the spindle – Sealing system: Prevents helium, auxiliary sealing Third, the typical turbocharger technology introduced After more than 100 years of development, the turbocharger has been very mature, and various new technologies have emerged. From the original pure supercharging, a bypass valve supercharger, a two-stage supercharger system, and electronic control have been developed. Variable section VGT supercharger. Here are some typical turbochargers: 1, with bypass valve booster Taking the HOLSET as an example, the bypass valve controls the opening of the air valve at the turbine inlet through the pressure of the air outlet of the compressor, so that the turbine exhaust gas is exhausted from the bypass. Its purpose is to limit the supercharger speed at high engine speeds and high load conditions, and it can reduce the engine burst pressure at full load and high speed conditions. The turbocharger with bypass valve is simple in structure, low in cost, capable of both high and low speed operation, and is currently the most mature supercharger product. 2 Electronically controlled variable section VGT supercharger The variable section technology means that the turbine circulation capacity can be adjusted automatically during engine operation, which is a more effective and complicated turbocharging technology. This method ensures that regardless of the operating state of the engine, the energy generated by the exhaust turbine can just meet the driving of the compressor, and the combustion of the engine is controlled in a more ideal state. The core part of VGT technology is the guide vane with adjustable vortex section. The outer side of the turbine adds a guide vane whose angle can be controlled by the electronic system. The relative position of the guide vane is fixed, but the vane angle can be adjusted. When the system is working, the exhaust gas will be sent to the turbine blades along the guide vanes. By adjusting the angle of the blades, the flow rate and the flow rate of the gas flowing through the turbine blades are controlled so as to control the rotation speed of the turbine. In addition, since changing the blade angle can effectively control the rotation speed of the turbine, this also realizes the overload protection of the turbine. Therefore, the turbocharger using the VGT technology does not need to have a bleed valve. The electronically controlled variable section VGT supercharger has a complex structure, high cost, adjustable turbine cross-sectional area, and can take into account the full operating conditions, but the failure rate is relatively high. Its advantages are more accurate control, better emissions and fuel economy, and is currently used in Europe's Euro 6 engines, but it is less used because of cost and other reasons. 3 double booster The two-stage supercharger consists of two turbochargers of different specifications. The two turbochargers are connected in series and controlled by a bypass valve adjustment mechanism. When the engine speed is low, that is, when the exhaust gas volume is small, the bypass valve is completely closed, and all the exhaust gas flows into the small turbine to achieve rapid and efficient compression. When the engine speed increases, the bypass valve opens gradually and the compression work gradually shifts to the large turbine. Simply put, when the engine is running at a low speed, less exhaust gas can rotate the turbine with a lower driving pressure at a high speed to generate enough intake pressure; when the engine speed is increased, the compression work is mainly driven by a larger driving pressure. The turbine's commitment to continue to enter the state of high boost value, providing a strong and consistent power. The supercharger has a complex structure, a very high cost, and often has interstage cooling in the middle. The advantage is that the supercharging degree is higher, the maximum power of the same displacement engine is greater, and the balance between low speed and high speed working conditions is more Well, emissions and fuel economy are better. Huizhou City Melors Plastic Products Co., Limited , https://www.evadecking.com